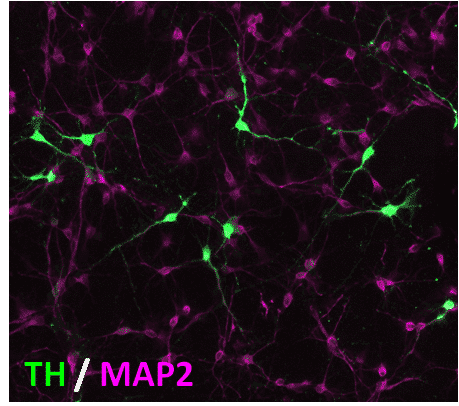
QPS Austria offers several cellular models comprising primary neurons or transgenic and non-transgenic cell lines to mimic disease related conditions. Cellular models offer the advantage of a controlled environment useful for exploring single pathogenic mechanisms and the proteins involved. Our models are fast and cost-efficient. Customized models are generated gladly on request.
- Abeta1-42
- MPP+
- 6-OHDA
- BSO
- シヌクレイン
- H2O2
- イオノマイシン
- オカダ酸
- NMDA 病変
- グルタミン酸病変
- ヨード酢酸
- シアン化ナトリウム
- 成長因子除去
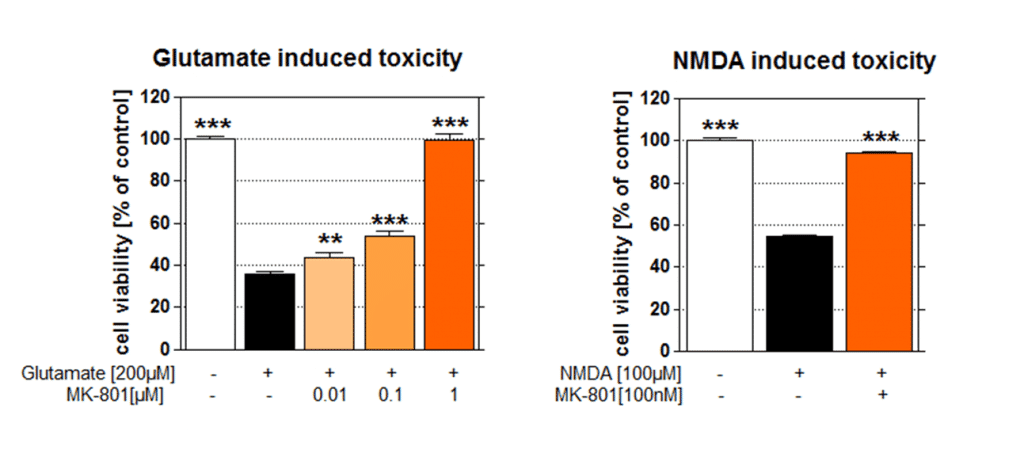
Excitotoxicity
Excitotoxicity is the pathological process by which neurons are damaged and killed by excessive stimulation by neurotransmitters such as glutamate. This occurs when receptors for the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate (glutamate receptors) such as the NMDA receptor and AMPA receptor are overactivated by glutamatergic storm. Excitotoxins like NMDA which bind to these receptors, or pathologically high levels of glutamate, can cause excitotoxicity by allowing high levels of calcium ions to enter the cell.
Excitotoxicity may be involved in stroke or traumatic brain injury and in neurodegenerative diseases of the central nervous system such as multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Parkinson’s disease, and also Huntington’s disease.