SOD1-G93A/low Mouse Model
SOD1-G93A/low mice express human SOD1 with the G93A mutation under control of the cistronic human SOD1 promotor, similar to SOD1-G93A mice but with a lower copy number. Mutations in this gene have been linked to familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS or Lou Gehrig’s disease). Animals develop a similar phenotype as the SOD1-G93A mouse model, but disease onset is delayed and start at about 6-7 months and thus extending the treatment window. Animals survive appr. 6 weeks after symptom onset. These mice are thus a valuable tool to study the influence of new drugs on neuromuscular disorders such as ALS.
The most important characteristics of SOD1-G93A/low mice are:
- Muscle weakness
- Motor deficits
- Reduced mean survival
- Increased plasma neurofilament light chain levels
- Neuroinflammation
Evaluation of astrocytosis by GFAP labeling shows an increased immunoreactive area in SOD1-G93A/low mice starting at the age of 27 weeks in the cervical ventral horn (Fig.1A), while GFAP levels increase in the thoracic and lumbar ventral horn starting at the age of 30 weeks (Fig.1B, C). Analysis of activated microglia by Iba1 labeling shows an immunoreactive area in SOD1-G93A/low mice starting at the age of 27 weeks in all three evaluated spinal cord regions (Fig.1A-C). SOD1-G93A/low mice thus present a robust neuroinflammatory spinal cord pathology at the age of 30 weeks (Fig.1).
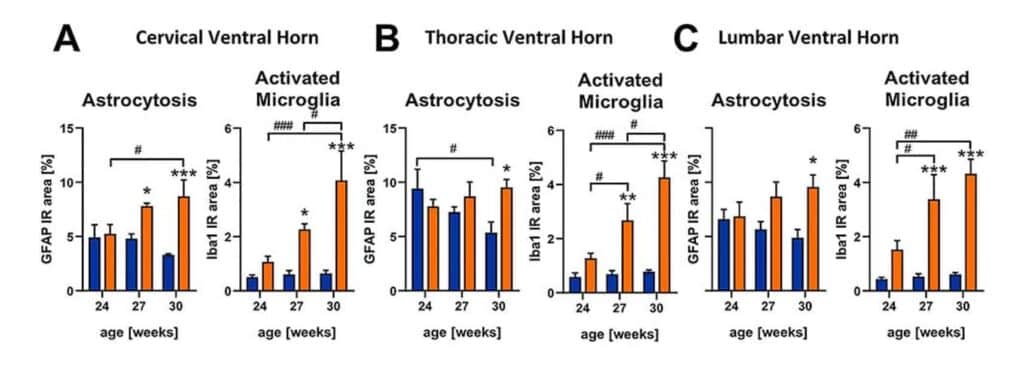
Figure 1: Astrocytosis and activated microglia in the spinal cord of SOD1-G93A/low mice at the age of 24 to 30 weeks. SOD1-G93A/low mice at the age of 24, 27 and 30 weeks were evaluated for GFAP and Iba1 expression in the cervical (A), thoracic (B) and lumbar (C) ventral horn compared to ntg littermates. Two-way ANOVA with Tukey‘s and Sidak’s multiple comparison post hoc test; n = 4 per group. Mean + SEM. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. *differences between genotypes; #differences between age groups.
Analysis of the plasma of SOD1-G93A/low mice show highly increased neurofilament light chain levels at the age of 24 weeks (Fig.2) suggesting that SOD1-G93A/low mice present a strong neurodegenerative pathology.
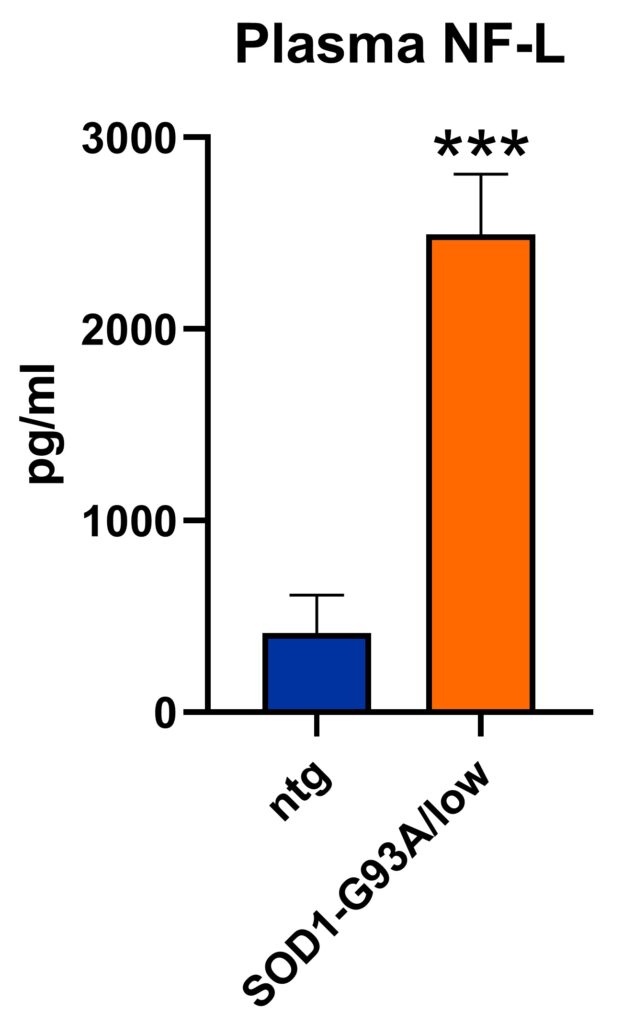
Figure 2: Neurofilament light chain (NF-L) levels in the plasma of SOD1-G93A/low mice. NF-L levels in the plasma of SOD1-G93A/low mice at the age of 24 weeks; SOD1-G93A/low: n = 6, ntg: n = 6; unpaired t-test. Mean + SEM. ***p<0.001.
QPS Neuropharmacology offers a custom-tailored study design for SOD1-G93A/low mice, and we are flexible to accommodate your special interests. We are also happy to advise you and propose study designs. SOD1-G93A/low mice show a relevant ALS phenotype at the age of 27 weeks. Furthermore, non-transgenic littermates are available as control animals needed for proper study design.
We are happy to evaluate the efficacy of your compound in the SOD1-G93A/low mouse model! The most common readouts are:
- Survival
- Clinical signs / Vercelli Score
- Motor deficits
- Muscle weakness
- SOD1 aggregates
- Oxidative Stress
- Neuroinflammation
